Industrial and societal challenges
· Recovery and protection of ore resources, industrial mineral resources and water resources;
· Development of clean and safe mineral-engineering procedures;
· Improving techniques for the recovery, recycling and stabilization of residues.
Industry partners: mine and quarry operators, equipment suppliers, reactive product suppliers, water treatment companies, and waste producers.
Scientific challenges
· Development and improvement of separation techniques:
The art of separation forms the very core of mineral engineering. Constituents must be separated from very complex mixtures, including crushed rock, solid aggregates, dry powders, fluid suspensions and wet matter.
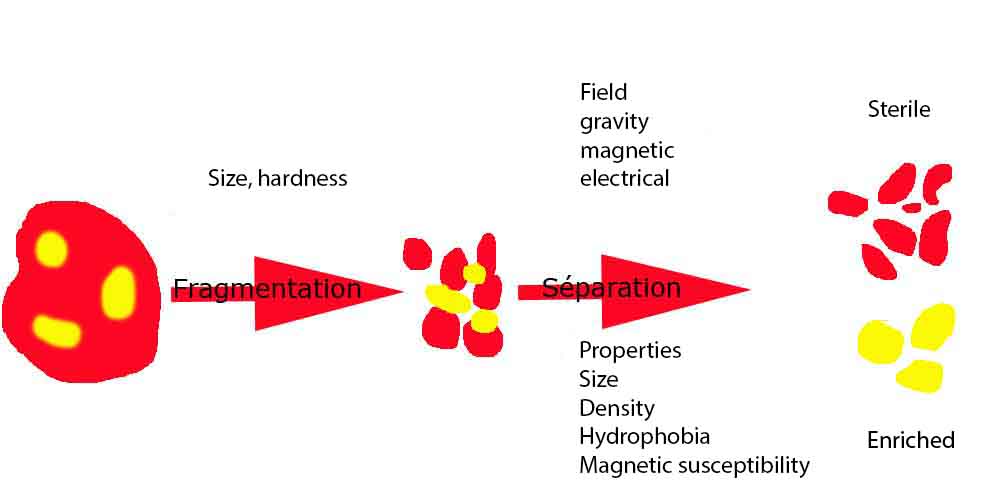
Successful separation requires not only an awareness of the properties of the material to be separated (for example, mineralogy, crystallinity, hardness, magnetic susceptibility, conductivity or the hydrophile-hydrophobe balance) but also knowledge of how external force-fields (gravity, centrifuge, vibration, magnetic and electrical forces) can be applied in relation to the contrast properties to enable partitioning of the different constituents.
Research conducted at the laboratory focuses on:
1. Identifying and characterising the different constituents of complex mixtures: Which characteristics are able to sufficiently differentiate one constituent from another and at what scale?
2. Modelling force fields: Which force-field can be linked to a specific characteristic in order to achieve separation? How can this force be generated? How can we monitor its structure? How does it interact with the material? What flow or flux should be associated with it?
3. Observing and modelling separation dynamics: How do the different constituents move about under the effect of the force-field? What are the characteristic timescales?
4. Identifying and characterising the separation products: Have the constituents actually been separated on the basis of the characteristic chosen? Do the constituents have the same properties as in the mixture?
· Developing new techniques for stabilization of waste and rendering it inert:
Developing effective confinement matrices
Controlling elementary/initial mobility and immediate mechanical strength/resistance
Evaluating residual reactivity and long-term changes
